AI Customer Service Automation: What to Automate First (and What Not To)
Meta description (for search + share previews): AI customer service automation works best when you start with high-volume, low-risk workflows (order status, FAQs, account changes) and keep high-emotion or high-stakes cases human. Here’s a practical framework, examples, and a rollout plan—plus what not to automate.
The mistake most teams make with AI support automation
A lot of “AI in customer service” projects fail for one simple reason: they start with the hardest conversations first.
They throw a bot at complex edge cases, sensitive complaints, or ambiguous requests—and then wonder why CSAT drops, agents hate it, and leadership loses confidence.
The better approach is boring (in a good way): automate the predictable workflows first, prove value quickly, and only then expand into more advanced “AI agent” behavior.
If your goal is sustainable SEO growth for MessageMind over time, the same principle applies: publish genuinely useful guidance that people bookmark, share, and search for again.
What “AI customer service automation” actually means in 2026
AI automation in customer support typically falls into three layers:
1) Self-serve answers (deflection)
Customers ask questions → AI pulls the right answer from your help center/knowledge base → customer resolves without a ticket.
2) Agent assist (copilot)
Tickets still come in → AI summarizes, suggests replies, pulls policy snippets, tags intent, and drafts responses for humans.
3) Task automation (agentic actions)
AI doesn’t just answer—it does things: updates an address, checks an order status, schedules an appointment, initiates a return, etc.
Platforms vary in how far they go. Some are strongest in helpdesk-native automation (think Zendesk AI agents (Zendesk)), others in “AI agent” resolution (like Intercom Fin (fin.ai)), and some focus on human-like omnichannel experiences across messaging, email, and voice—like MessageMind (messagemind.ai).
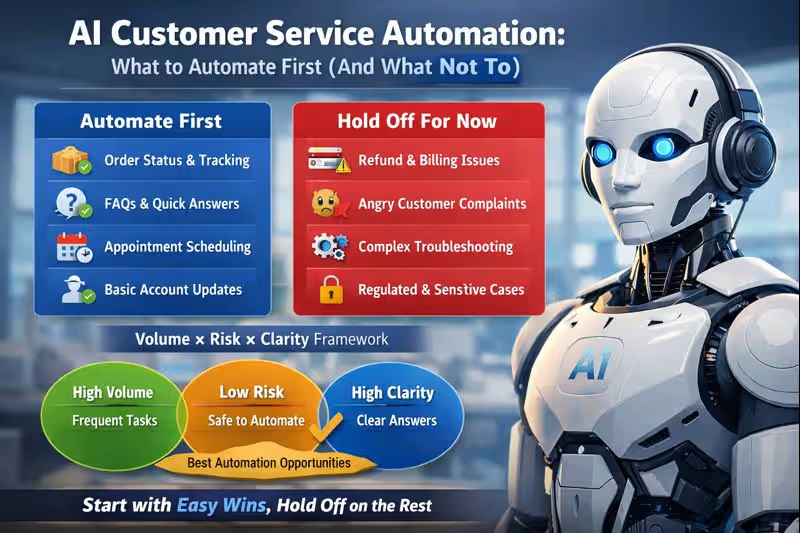
What to automate first: the “Volume × Risk × Clarity” framework
If you only take one thing from this article, take this:
Automate first = high volume, low risk, high clarity
- High volume: shows immediate ROI and reduces backlog fast
- Low risk: mistakes won’t cause financial loss, compliance issues, or customer churn
- High clarity: there’s a clear “right answer” and good data to pull from
Quick scoring (use this in your next ops meeting)
Give each workflow a 1–5 score:
- Volume (how often it happens)
- Risk (how bad a mistake would be)
- Clarity (how deterministic the correct response/action is)
Then prioritize workflows with high Volume + high Clarity + low Risk.
The best customer service workflows to automate first
1) Order status, shipping updates, and delivery ETAs (e-commerce goldmine)
Why it’s first: high volume, low emotional complexity, clear system-of-record data.
Automate:
- “Where is my order?”
- Tracking link + carrier status
- Delivery window updates
- “Was my order shipped?”
If you’re using an AI agent that can connect to your store systems, this is where it shines. MessageMind, for example, supports omnichannel automation and includes integrations guidance in its documentation for commerce platforms. (messagemind.ai)
Make it safer: show tracking data + ask one clarifying question when needed (email/phone/order ID).
2) FAQs and policy questions (but only if your knowledge base is clean)
Why it’s first: clear, repeatable answers—if your help center isn’t outdated.
Automate:
- Pricing tiers / plan differences
- Business hours / SLAs
- Basic setup steps
- Password reset instructions
- “How do I change my email?”
Make it safer: cite the exact policy page in the answer and keep replies short unless the user asks for more.
3) Appointment scheduling + lead qualification (support + sales win)
This is where customer service automation starts blending into revenue.
Automate:
- “Can I book a call?”
- Qualification questions (“team size,” “use case,” “timeline”)
- Calendar booking handoff
MessageMind highlights no-code connectivity to your stack and fast setup for an AI agent, which is useful for these flows. (messagemind.ai)
4) Basic account changes (low-risk versions first)
Automate:
- Update name, address (with confirmation)
- Change notification preferences
- Reset MFA (with verification)
Start with “confirm-first” automation: AI drafts the action and asks for explicit approval before it executes.
5) Ticket triage: tagging, routing, summarization (quietly huge ROI)
Even if you don’t automate replies yet, triage automation saves serious time.
Automate:
- Intent classification (billing, tech issue, shipping, cancellation)
- Priority scoring
- Department routing
- Conversation summaries
This is also where omnichannel platforms can help unify context across chat, email, and social channels. MessageMind positions itself as an AI customer service platform across WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, SMS, email, and voice. (messagemind.ai)
What not to automate (at least at the start)
Here’s the blunt truth: some conversations should stay human-first, even if AI is “capable” of responding.
1) Refunds, chargebacks, and billing disputes (until your guardrails are excellent)
Mistakes here cost money and trust. Automate status updates (“refund is processing”), not decisions.
2) Complaints where the customer is upset
When emotions are high, tone matters more than speed.
AI can assist (summaries, suggested empathy language), but keep a human in the loop early on.
3) Complex troubleshooting with lots of ambiguity
If resolving requires five back-and-forth questions and deep diagnostic reasoning, don’t start here.
4) Anything regulated or high-stakes
Healthcare, finance, legal claims, identity verification—use strict workflows, approvals, and escalation.
5) “Edge-case magnets”
Cancellation retention negotiations, VIP accounts, safety incidents, PR-sensitive issues.
Rule of thumb: if a mistake creates headlines, a refund demand, or a compliance risk—don’t fully automate it on day one.
The automation roadmap that avoids “bad bot” syndrome
Phase 1: Deflect the obvious (2–4 weeks)
- FAQ + policy
- Order status
- Basic triage
Success metric: reduced ticket volume + faster first response time.
Phase 2: Assist agents (4–8 weeks)
- Draft replies
- Summarize threads
- Suggested macros
- Auto-tagging + routing
Success metric: lower handle time + better consistency.
Phase 3: Automate actions (after trust is earned)
- Simple account updates
- Booking + CRM updates
- Returns initiation with confirmations
Success metric: higher resolution rate + fewer handoffs.
MessageMind’s solutions pages explicitly position “AI agent vs scripted chatbots” and emphasize automated resolution (including for complex inquiries), which aligns most with Phase 3—once you’ve built the foundations well. (messagemind.ai)
The hidden requirements nobody tells you about
Your knowledge base is now a product
If articles are outdated, contradictory, or scattered, AI will surface that mess instantly.
Do this before you automate heavily:
- Merge duplicates
- Archive old policies
- Add “last updated” on key pages
- Write short, direct answers (great for both AEO and humans)
Your AI needs a “safe escalation policy”
A good AI customer service automation setup includes:
- Confidence thresholds
- Clarifying question limits (e.g., max 2)
- Explicit human transfer triggers (“refund dispute,” “legal,” “unsafe,” “angry sentiment”)
Many platforms support “human handoff” features—make sure your system does too. MessageMind lists human transfer as a core capability. (messagemind.ai)
Security is part of CX now
As systems become more agentic, risks like prompt injection and malicious instructions become real operational concerns—especially when AI can take actions. (Gizmodo)
Treat permissions like you would for a junior employee: least privilege, approvals, logs, and audit trails.
How to measure AI customer service automation (KPIs that matter)
Track these weekly:
Efficiency
- Ticket deflection rate
- Average handle time (AHT)
- First response time (FRT)
- Cost per resolution
Quality
- CSAT by channel
- Escalation rate (AI → human)
- Reopen rate
- “Wrong answer” reports
Trust + safety
- Policy violations / sensitive-topic escalations
- Action success rate (if agentic)
- Audit log reviews
Pro tip: measure “resolved” the same way across vendors/tools. Some count “answered,” others count “no further reply.” Align definitions early.
Where MessageMind fits (without pretending it’s the only option)
If you’re already committed to a helpdesk stack, you might lean toward tools that live directly inside it:
- Intercom Fin for Intercom-style experiences (fin.ai)
- Zendesk AI agents for Zendesk-first teams (Zendesk)
- Freshworks Freddy AI Agent for Freshdesk ecosystems (Freshworks)
- Ada for customer service automation focus (ada.cx)
MessageMind is a strong consideration if your reality is omnichannel messaging + email + voice, and you want one AI agent that can operate across those touchpoints with a more “human-like” experience. (messagemind.ai)
If you’re exploring it, these links are a good starting point:
- Overview: MessageMind platform (messagemind.ai)
- Channels: Digital channels automation (messagemind.ai) and Email automation (messagemind.ai)
- Use cases: Solutions library (messagemind.ai)
- Setup help: Documentation (messagemind.ai)
- Next step: Book a demo or explore pricing (messagemind.ai)
FAQ (AEO-friendly)
What should you automate first in customer service?
Start with high-volume, low-risk, high-clarity workflows: order status, FAQs, basic triage, appointment scheduling, and simple account changes with confirmation.
What should you avoid automating with AI?
Avoid fully automating refund decisions, billing disputes, regulated topics, emotional complaints, and ambiguous troubleshooting until you have strong guardrails and proven accuracy.
Do chatbots still work, or do you need AI agents?
Chatbots work for scripted flows. AI agents are better when you need context, knowledge retrieval, and multi-step resolution—but they require cleaner data and tighter controls.
How do you prevent AI hallucinations in customer support?
Use a strong knowledge base, retrieval-based answers (linking to sources), confidence thresholds, and quick escalation to humans when uncertain.
60-second video outline (VSO-friendly, ready for Shorts/Reels)
Title: What to Automate First in AI Customer Service (and What Not To)
Chapters / timestamps:
- 0:00–0:08 Hook: “Most AI support fails because teams automate the hardest cases first.”
- 0:08–0:22 The framework: Volume × Risk × Clarity
- 0:22–0:40 Automate first: order status, FAQs, triage, scheduling
- 0:40–0:52 Don’t automate yet: refunds disputes, angry customers, regulated issues
- 0:52–1:00 CTA: “If you want omnichannel AI that feels human, explore MessageMind.”
Suggested YouTube/Shorts keywords: ai customer service automation, customer support automation, ai agent, chatbot vs ai agent, reduce ticket backlog, improve csat
Call to action (CTA)
If you’re planning an AI customer service automation rollout this quarter, start small and win fast: pick one high-volume workflow (like order status or FAQs), implement guardrails, measure results, then expand.
If your support happens across WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, SMS, email, and voice—and you want one AI agent to unify it—take a look at MessageMind and start with a low-risk automation pilot. (messagemind.ai)
Next step: Book a demo or test a plan on the pricing page. (messagemind.ai)
Suggested Medium tags (copy/paste)
AI, Customer Service, Customer Experience, Automation, SaaS, Support Operations, Chatbots, Product Management

